Quinoa, a nutritious and versatile superfood, grows in a fascinating way that has intrigued many. How does quinoa grow? The answer lies in its origin as a hardy plant that thrives in diverse climates and soil conditions. From tiny seeds planted in the earth, quinoa sprouts delicate green leaves, reaching for the sun. As it matures, the plant forms clusters of vibrant flowers that eventually give way to the prized quinoa seeds we enjoy. Join us as we delve deeper into the captivating journey of how quinoa grows.
How Does Quinoa Grow: A Comprehensive Guide
Welcome, young minds, to a fascinating journey into the world of quinoa! Have you ever wondered how this nutritious and delicious grain-like crop grows? Join me as we explore the secrets behind the cultivation of quinoa and learn how this ancient crop makes its way from seed to table.
The Origins of Quinoa
Quinoa, pronounced keen-wah, has been grown for thousands of years in the Andean region of South America. It was a staple food for the ancient Inca civilization and is now celebrated worldwide for its health benefits and versatility in cooking. So, how does this superfood make its way from a tiny seed to a bountiful harvest?
Planting Quinoa Seeds
Quinoa plants prefer cool, dry conditions, making them well-suited to high-altitude regions. Farmers begin the process by planting quinoa seeds in well-drained soil during the spring months. The seeds are small and can vary in color from white to red or black, depending on the variety.
Once the seeds are sown, they require consistent watering to help them germinate and sprout. Quinoa plants have delicate roots that need moisture to grow, so farmers carefully monitor the soil to ensure the seeds have enough water without becoming waterlogged.
Growth and Development of Quinoa Plants
As the quinoa plants continue to grow, they develop striking green leaves and tall, slender stems. The plants can reach heights of up to six feet, swaying gently in the breeze as they soak up the sunlight. Quinoa plants are resilient and can thrive in diverse environments, making them a popular choice for sustainable farming practices.
One of the fascinating aspects of quinoa cultivation is its ability to adapt to varying climates and soil conditions. Whether grown in the mountains of the Andes or the plains of North America, quinoa has a remarkable capacity to flourish and produce nutritious seeds.
Flowering and Seed Formation
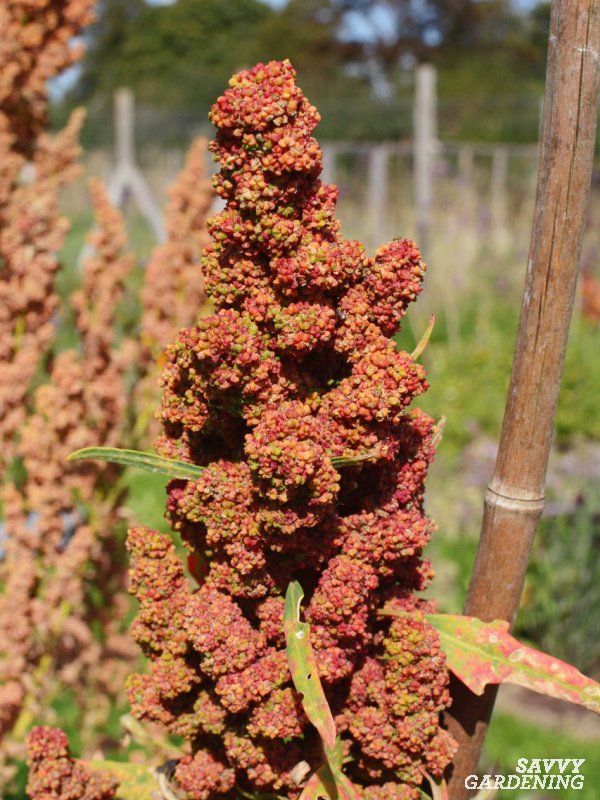
As the quinoa plants mature, they begin to produce delicate clusters of flowers. These flowers can range in color from white to pink or purple, adding a vibrant touch to the field where they grow. Bees and other pollinators play a crucial role in fertilizing the flowers, ensuring the development of healthy seeds.
Once the flowers are pollinated, they give way to seed pods that contain the quinoa grains. These seed pods slowly ripen and change color, indicating that the seeds are ready for harvest. Farmers carefully monitor the progression of the seeds, waiting for the perfect moment to begin the harvesting process.
Harvesting Quinoa Seeds
Harvesting quinoa seeds is a labor-intensive process that requires precision and care. Farmers typically wait until the majority of the seed pods have turned a golden hue before beginning the harvest. Using specialized tools, they gently cut the seed heads from the plants and collect them in baskets or bins.
Once the seed heads are gathered, they are left to dry in the sun to reduce moisture levels and ensure the seeds are preserved properly. This drying process is essential for storing quinoa seeds long-term and maintaining their quality for consumption.
The Importance of Quinoa in Agriculture
Quinoa is not only a valuable crop for its nutritional benefits but also for its role in sustainable agriculture. Unlike many other grains, quinoa is naturally resistant to pests and diseases, reducing the need for chemical pesticides. Additionally, quinoa plants have a deep root system that helps prevent soil erosion, making them a beneficial crop for maintaining soil health.
By cultivating quinoa, farmers can improve the biodiversity of their fields and promote a more environmentally friendly approach to agriculture. The resilience of quinoa plants makes them a valuable asset in the face of climate change, offering stability and security to food systems around the world.
So, dear readers, now you know the incredible journey of how quinoa grows from a tiny seed to a nutritious grain ready to nourish our bodies. The next time you enjoy a delicious quinoa salad or bowl of quinoa porridge, remember the hard work and dedication that goes into cultivating this remarkable crop. Quinoa truly is a gift from nature, providing us with sustenance and joy in every bite.
As you continue to explore the wonders of the natural world, let the story of quinoa inspire you to appreciate the beauty and complexity of plant life. May we always remember to care for the earth and cherish the bountiful harvests it provides. Until next time, happy growing!
How to Grow and Harvest Quinoa – Vancouver, Canada
Frequently Asked Questions
How is quinoa grown?
Quinoa is typically grown as a crop in regions with cool, dry climates. It thrives best at high altitudes with temperatures ranging from 25 to 32 degrees Celsius. The quinoa plant grows best in sandy, well-drained soils and requires adequate sunlight for optimal growth.
What is the planting process for quinoa?
Quinoa seeds are planted directly into the soil, either by sowing them by hand or using specialized seeding equipment. The seeds are usually sown in rows to facilitate irrigation and harvesting. It is essential to plant the seeds at the right depth and spacing to ensure proper germination and growth.
How long does it take for quinoa to mature?
Quinoa plants typically take around 90 to 120 days to reach maturity from the time of planting. The exact time may vary depending on environmental conditions such as temperature, soil quality, and water availability. Harvesting is usually done when the plant’s leaves turn yellow and the seeds have dried.
What are the potential challenges in growing quinoa?
While quinoa is a hardy crop, it can face challenges such as pests, diseases, and adverse weather conditions. Pests like aphids and birds can damage the crop, while diseases such as powdery mildew and blight can affect plant health. Additionally, extreme temperatures or water stress can impact quinoa growth.
Final Thoughts
Quinoa grows best in well-drained soil and requires minimal water, making it a sustainable crop. This versatile grain thrives in diverse climates, from the Andes to North America. Farmers cultivate quinoa for its high nutritional value and resilience to harsh conditions. Understanding how quinoa grows is essential for maximizing its potential as a staple food worldwide.